- 您现在的位置:买卖IC网 > Sheet目录346 > NCP5007SNT1 (ON Semiconductor)IC LED DRIVR WHT COMPACT 5TSOP
�� �
�
NCP5007�
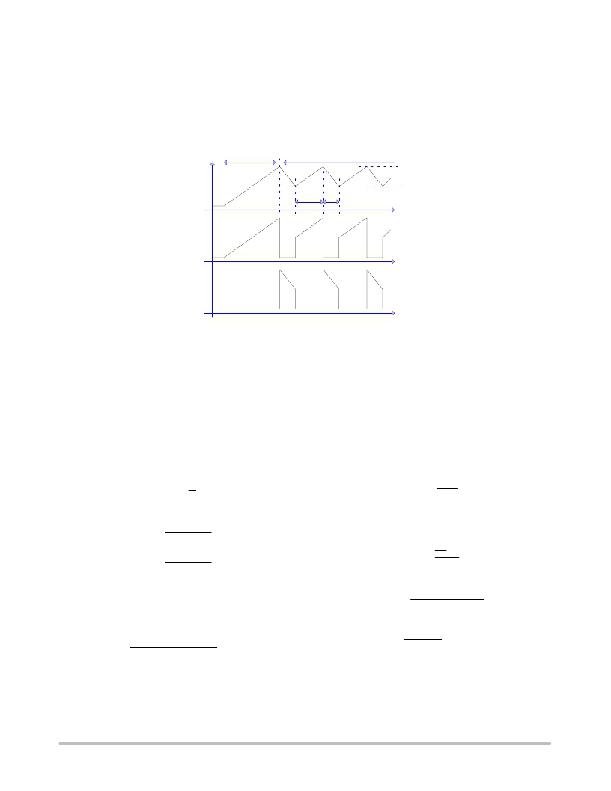
�Basically,� the� chip� operates� with� two� cycles:�
�Cycle� #1� :� time� t1,� the� energy� is� stored� into� the� inductor�
�Cycle� #2� :� time� t2,� the� energy� is� dumped� to� the� load�
�The� POR� signal� sets� the� flip?flop� and� the� first� cycle� takes�
�place.� When� the� current� hits� the� peak� value,� defined� by� the�
�error� amplifier� associated� with� the� loop� regulation,� the�
�First� Startup�
�I� L�
�flip?flop� resets,� the� NMOS� is� deactivated� and� the� current� is�
�dumped� into� the� load.� Since� the� timing� is� application�
�dependent,� the� internal� timer� limits� the� Toff� cycle� to� 320� ns�
�(typical),� making� sure� the� system� operates� in� a� continuous�
�mode� to� maximize� the� energy� transfer.�
�Normal� Operation�
�Ipeak�
�Iv�
�0� mA�
�t1�
�t2�
�t�
�Ids�
�0� mA�
�Io�
�0� mA�
�Figure� 4.� Basic� DC?DC� Operation�
�t�
�t�
�Based� on� the� data� sheet,� the� current� flowing� into� the�
�inductor� is� bounded� by� two� limits:�
�?� Ipeak� Value:� Internally� fixed� to� 350� mA� typical�
�?� Iv� Value:� Limited� by� the� fixed� Toff� time� built� in� the�
�chip� (320� ns� typical)�
�The� system� operates� in� a� continuous� mode� as� depicted� in�
�Figure� 4� and� t� 1� &� t� 2� times� can� be� derived� from� basic�
�equations.� (Note:� The� equations� are� for� theoretical� analysis�
�only,� they� do� not� include� the� losses.)�
�Of� course,� from� a� practical� stand� point,� the� inductor� must�
�be� sized� to� cope� with� the� peak� current� present� in� the� circuit�
�to� avoid� saturation� of� the� core.� On� top� of� that,� the� ferrite�
�material� shall� be� capable� to� operate� at� high� frequency�
�(1.0� MHz)� to� minimize� the� Foucault’s� losses� developed�
�during� the� cycles.�
�The� operating� frequency� can� be� derived� from� the�
�electrical� parameters.� Let� V� =� Vo� ?� V� bat� ,� rearranging�
�Equation� 1:�
�E� +� L� *� di�
�ton� +� dI� *� L�
�dt�
�(eq.� 1)�
�E�
�(eq.� 5)�
�Let� E� =� V� bat� ,� then:�
�t1� +�
�(Ip� *� Iv) * L�
�Vbat�
�(eq.� 2)�
�Since� toff� is� nearly� constant� (according� to� the� 320� ns�
�typical� time),� the� dI� is� constant� for� a� given� load� and�
�inductance� value.� Rearranging� Equation� 5� yields:�
�t2� +�
�(Ip� *� Iv)� *� L�
�Vo� *� Vbat�
�*L�
�ton� +�
�(eq.� 6)�
�(eq.� 3)�
�Since� t� 2� =� 320� ns� typical� and� Vo� =� 22� V� maximum,� then�
�V*dt�
�L�
�E�
�Let� E� =� V� bat� ,� and� Vopk� =� output� peak� voltage,� then:�
�D� I� +�
�ton� +�
�(assuming� a� typical� V� bat� =� 3.0� V):�
�t2 * (Vo� *� Vbat)�
�L�
�(Vopk� *� Vbat) * dt�
�Vbat�
�Finally,� the� operating� frequency� is:�
�(eq.� 7)�
�F� +�
�1�
�ton� )� toff�
�D� Imax� +�
�320e� *� 9� * (22� *� 3.0)�
�22e� *� 6�
�+� 276� mA�
�(eq.� 4)�
�(eq.� 8)�
�The� output� power� supplied� by� the� NCP5007� is� limited� to�
�one� watt:� Figure� 5� shows� the� maximum� power� that� can� be�
�delivered� by� the� chip� as� a� function� of� the� input� voltage.�
�http://onsemi.com�
�6�
�发布紧急采购,3分钟左右您将得到回复。
相关PDF资料
NCP5008DMR2
IC LED DRVR WHT BCKLT 10MICROSMD
NCP5010FCT1G
IC LED DRVR WHT BCKLT 8-FLIPCHIP
NCP5021MUTXG
IC WHITE LED DVR HV AMB 16-UQFN
NCP5050MTTXG
IC LED DRIVR PHOTO FLASH 10-WDFN
NCP5111DR2G
IC DRIVER HI/LOW SIDE HV 8-SOIC
NCP5304DR2G
IC DRIVER HI/LOW SIDE HV 8-SOIC
NCP5355DG
IC DRVR SYNC BUCK MOSF 12A 8SOIC
NCP5359ADR2G
IC MOSFET GATE DVR DUAL 8-SOIC
相关代理商/技术参数
NCP5007SNT1G
功能描述:LED照明驱动器 White LED Backlight Boost RoHS:否 制造商:STMicroelectronics 输入电压:11.5 V to 23 V 工作频率: 最大电源电流:1.7 mA 输出电流: 最大工作温度: 安装风格:SMD/SMT 封装 / 箱体:SO-16N
NCP5008
制造商:ONSEMI 制造商全称:ON Semiconductor 功能描述:AC-DC Offline Switching Controllers/Regulators
NCP5008/D
制造商:ONSEMI 制造商全称:ON Semiconductor 功能描述:White LED Driver
NCP5008_06
制造商:ONSEMI 制造商全称:ON Semiconductor 功能描述:Backlight LED Boost Driver
NCP5008DMR2
功能描述:LED照明驱动器 15V Output Max LED RoHS:否 制造商:STMicroelectronics 输入电压:11.5 V to 23 V 工作频率: 最大电源电流:1.7 mA 输出电流: 最大工作温度: 安装风格:SMD/SMT 封装 / 箱体:SO-16N
NCP5008DMR2G
功能描述:LED照明驱动器 15V Output Max LED Backlight RoHS:否 制造商:STMicroelectronics 输入电压:11.5 V to 23 V 工作频率: 最大电源电流:1.7 mA 输出电流: 最大工作温度: 安装风格:SMD/SMT 封装 / 箱体:SO-16N
NCP5009
制造商:ONSEMI 制造商全称:ON Semiconductor 功能描述:Backlight LED Boost Driver
NCP5009DMR2
功能描述:IC LED DRVR WHT BCKLT 10MICROSMD RoHS:否 类别:集成电路 (IC) >> PMIC - LED 驱动器 系列:- 标准包装:1 系列:- 恒定电流:- 恒定电压:- 拓扑:PWM,切换式电容器(充电泵) 输出数:1 内部驱动器:是 类型 - 主要:背光 类型 - 次要:白色 LED 频率:642kHz 电源电压:2.7 V ~ 5.5 V 输出电压:5V 安装类型:表面贴装 封装/外壳:10-VFDFN 裸露焊盘 供应商设备封装:10-VSON 包装:剪切带 (CT) 工作温度:-30°C ~ 85°C 产品目录页面:1371 (CN2011-ZH PDF) 其它名称:BD1603NUV-E2CT